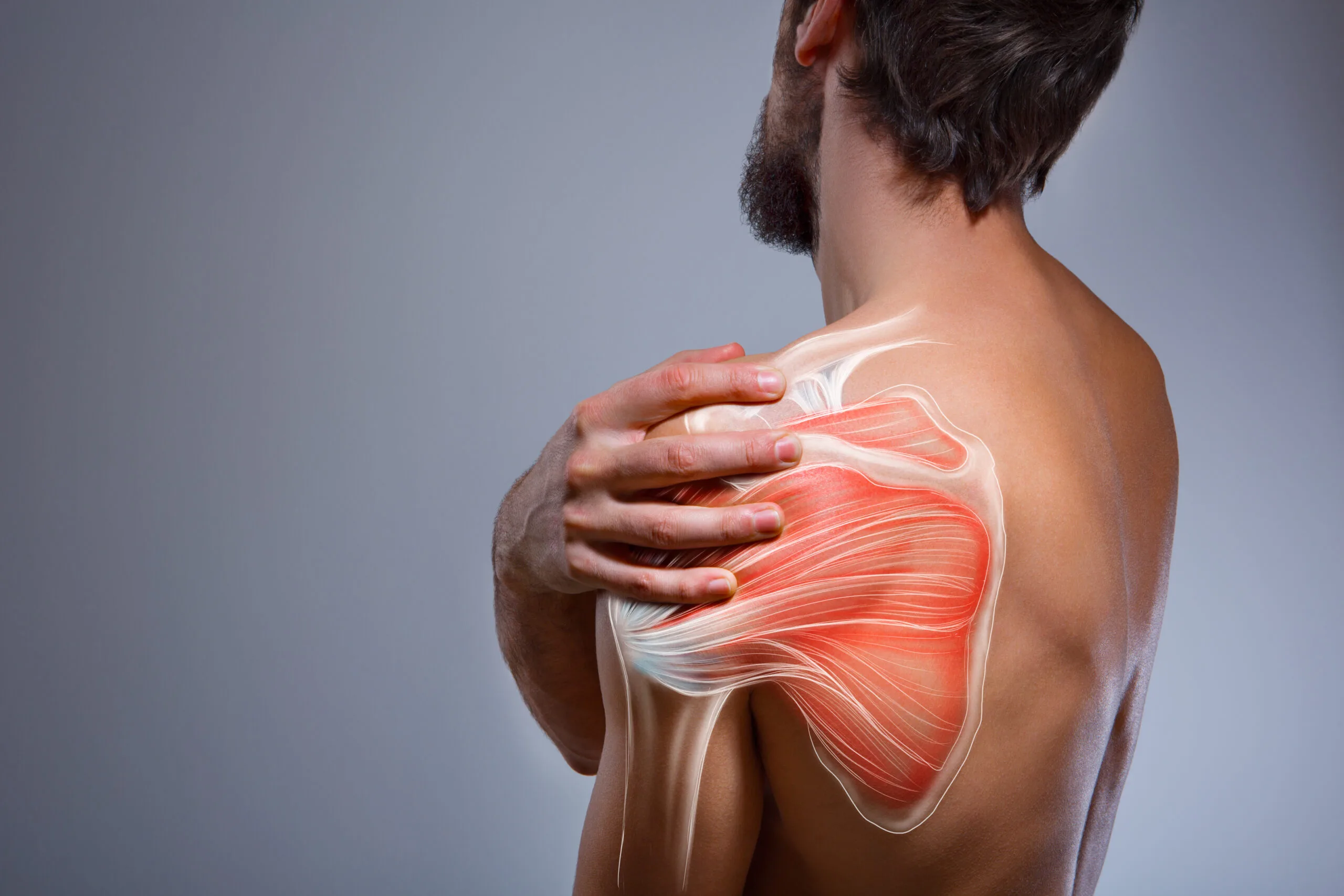
Shoulder pain can be debilitating, affecting our ability to perform daily activities and impacting our quality of life. Two common causes of shoulder pain are post-traumatic injuries and degenerative conditions related to age and diabetes mellitus. In this blog, we will explore these types of shoulder pain, their underlying causes, and the available treatment options.
1. Post-Traumatic Shoulder Pain:
Post-traumatic shoulder pain refers to pain and discomfort in the shoulder following an injury or trauma. It can result from various incidents such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents. Common injuries include fractures, dislocations, rotator cuff tears, and ligament sprains.
When experiencing post-traumatic shoulder pain, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. After a thorough physical examination, your healthcare provider may recommend scans and investigations such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to assess the extent of the injury. These diagnostic tools help identify the specific structures affected and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment for post-traumatic shoulder pain depends on the severity and nature of the injury. In some cases, conservative approaches like rest, ice, pain medications, and physiotherapy may be sufficient to alleviate pain and restore function. However, more severe injuries may require surgical intervention, such as fracture fixation, ligament repair, or rotator cuff surgery, to promote proper healing and long-term recovery.
2. Degenerative Shoulder Pain:
Degenerative shoulder pain is often associated with the natural aging process and conditions like diabetes mellitus. As we age, the structures within our shoulder joint, including cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, may undergo wear and tear. Diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic condition, can also contribute to the degeneration of these structures.
Individuals with degenerative shoulder pain often experience symptoms such as chronic, dull aching pain, limited range of motion, and difficulty performing overhead activities. These symptoms may worsen with prolonged use or repetitive movements.
If you are experiencing degenerative shoulder pain, it is advisable to consult an orthopedic or a healthcare professional specializing in musculoskeletal conditions. They will perform a comprehensive evaluation, which may include physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans, to assess the extent of degeneration and identify any associated complications.
Treatment for degenerative shoulder pain focuses on relieving pain, improving joint function, and enhancing quality of life. Non-surgical interventions may include medications for pain management, physiotherapy, and targeted exercises to improve strength and flexibility. In some cases, corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections may be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Surgical options, such as shoulder arthroscopy or joint replacement surgery, may be considered for individuals with severe degeneration and significant functional impairment. These procedures aim to repair or replace damaged structures within the shoulder joint, providing long-term relief and improved mobility.
In conclusion, post-traumatic shoulder pain and degenerative shoulder pain are two distinct types of shoulder conditions with different underlying causes. While post-traumatic injuries require prompt diagnosis through scans and investigations, degenerative shoulder pain related to age and diabetes mellitus is typically managed through conservative measures initially. With appropriate medical intervention, including medications, physiotherapy, and, in some cases, surgical interventions, individuals suffering from shoulder pain can find relief and regain function. If you are experiencing shoulder pain, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.